6. DA1459x Connecting The Board
6.1. Introduction
This section describes the installation procedure for the drivers, the configuration of the serial port, and all necessary steps to verify the connection with the PC as well as solutions to any problems that may occur.
6.2. Requirements of the Development PC
For proper evaluation and application development using the DA1459x SoC and the DEVKIT-PRO an external host is required. This external host must have an operating system already installed (Windows or Linux) and USB ports as described in Section 2.
6.3. Driver installation
6.3.1. Microsoft Windows
On first connection to a host PC running Microsoft Windows, the system will detect several devices and will automatically install all necessary drivers.
When the driver installation is complete, the system displays a Microsoft window similar to the one presented in Figure 6.
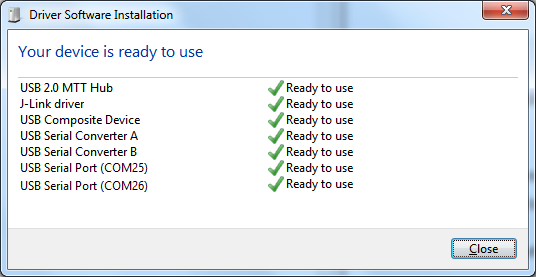
Figure 6 Windows driver installation
There are two virtual COM ports created by the Windows driver. The first COM port (lower number, COM25 in this example) provides a UART interface between the PC and the DA1459x device. The second (higher number, COM26 in this example) is used to export measurement data from the current sense circuitry on the DEVKIT-PRO to the Power Profiler tool. For more information on the Power Profiler, see the SmartSnippets Toolbox User Manual (UM-B-083).
Note
The COM port numbers assigned to the DEVKIT-PRO motherboard might be different than the ones shown in Figure 6.
The COM port numbers can be found in the Windows Device Manager (Control Panel > Device Manager > Ports (COM & LPT)) as shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7 Device Manager Ports
6.3.2. Linux
When DEVKIT-PRO is connected to a host PC running a Linux distribution (such as Ubuntu or CentOS) and has Internet connectivity, the system will detect several devices and all necessary drivers will be silently installed. Provided that the process has properly finished, two additional devices will appear in the /dev directory under the names ttyUSB0 and ttyUSB1, as shown in Figure 8. These names might be different in case other serial converters are connected to the system beforehand. If no other serial port converters are connected, the device that should be used with the terminal or programmer utility will be called /dev/ttyUSB0. If there are more devices with the name ttyUSBx, note which ones showed up when the DEVKIT-PRO was connected and use the lower number of the two devices.
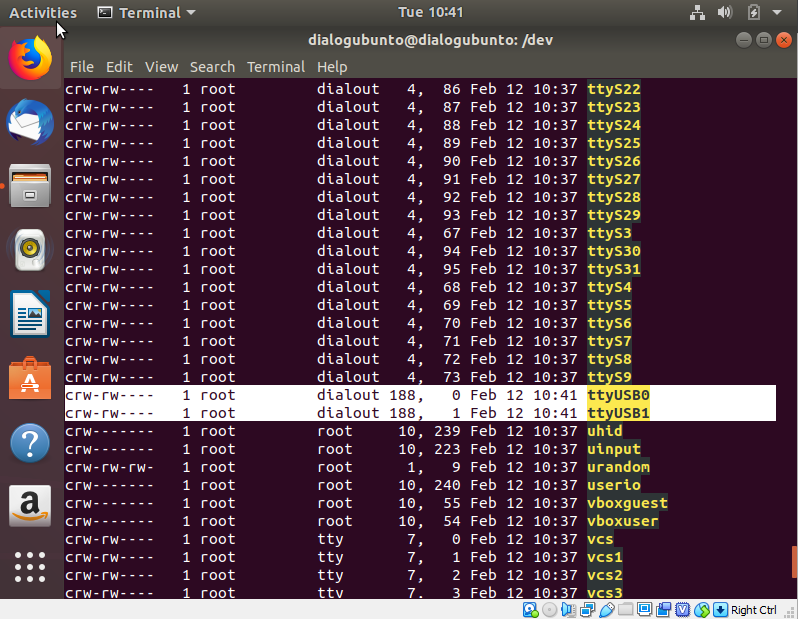
Figure 8 Ports assigned to DEVKIT-PRO
6.3.3. COM port usage
There are two virtual COM ports created by the driver with either Windows or Linux.
The first (lower number) is used to export a UART from the DA1459x device.
In the previous sections this was either COM25 or /dev/ttyUSB0. The second (higher number)
is used to export measurement data from the current sense circuitry on the DEVKIT-PRO to the Power Profiler tool.
6.3.4. Windows Host
On a Windows Host the utility Tera Term can be used to fully validate the connection to the DEVKIT-PRO.
Tera Term is a free software terminal emulator (communication program) which supports multiple communication protocols, including Serial port connections. Download Teraterm from https://ttssh2.osdn.jp. Run the teraterm-x.yy.exe and follow the installation wizard.
To make sure that the communication between the DEVKIT-PRO board and the development host is properly established, it is necessary to verify the UART connection between the two nodes. To do so, execute the following steps:
Step 1 Connect the DEVKIT-PRO USB1 connector to the PC via a USB cable Figure 1.
Step 2 Verify that the host discovered two serial ports – the first is connected to UART2 (see section Section 6.3.1).
Step 3 Open Tera Term from the Windows Start menu.
Step 4 In the Tera Term: New connection dialog, select Serial, then select the COM Port to use, and click OK.
Step 5 Select Setup > Serial Port as shown in Figure 9 and configure your UART port using the parameters as shown in Table 4.
Step 6 Open the Lowest COM port number assigned to the DEVKIT-PRO, refer to Figure 7 to figure out which port number is used by Windows by running the Windows Device Manager. Make sure that the UART is configured as shown in the Table 4.
Step 7 Press the reset button on the daughterboard (Figure 3)
Step 8 Once you have a connection, you should start to see something as shown in Figure 9. Besides the ‘Proximity Reporter’ text it will display the device’s unique Bluetooth address and the alert status. The LED on the daughterboard will blink with a very low frequency and the system starts advertising as’Renesas PX Reporter’
Settings |
Values |
|---|---|
Baud rate |
115200 |
Data bits |
8 |
Parity |
None |
Stop bits |
1 |
Handshaking |
None |
Warning
To get the control of the COM port You need to be an administrator on your local machine.

Figure 9 Terminal output via Tera Term (Windows)
6.3.5. Linux Host
Under Linux there is a simpler approach to validate the connection using
a basic terminal such as putty. Connect putty to /dev/ttyUSB0 at 115200
baud using this linux command sudo putty /dev/ttyUSB0 -serial -sercfg 115200,8,n,1,N
or run putty as shown in Figure 10

Figure 10 Setting port and testing connectivity in Linux
Once you have a connection, you should start to see something as shown in Figure 9.
6.4. Troubleshooting
If there are any problems with the DEVKIT-PRO connection to PC some possible solutions might be:
Make sure that the Host PC is connected to Internet
Make sure that no old FTDI drivers are installed. Drivers are available from the FTDI website.
Check for possible cabling issue by using a different USB cable
Connect the two elements using a different USB port on the host PC
Note
If none of these actions resolved the issue, please contact Renesas Engineering Community.