Architecture
Framework Overview
The intent of this library is to provide a python interface similar to SDK10 for controlling BLE of DA14xxx devices.
The BLE Framework implemented in SDK10 is depicted below:
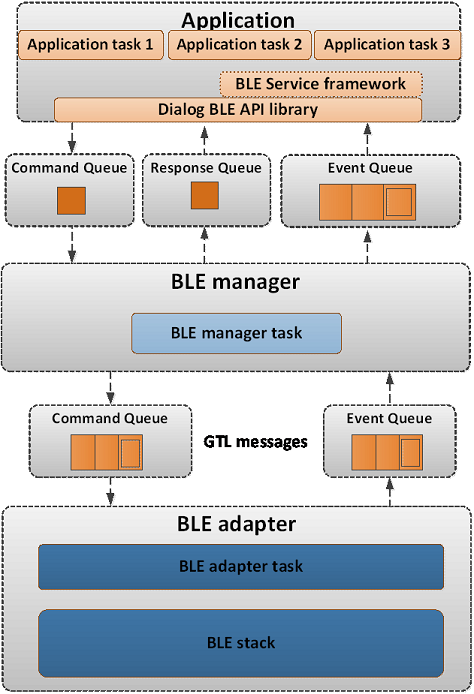
In SDK10, FreeRTOS is used as an operating system. FreeRTOS provides prioritized scheduling of tasks as well as primitives for communication between tasks such as queues, mutexes, semaphores, etc.
This library provides a python implementation for several layers of the SDK10 BLE Framework (e.g. the BLE Service Framework, Dialog BLE API Library, BLE Manager, and BLE Adapter).
The python threading library is used to achieve concurrency between tasks as well as provide communication primitives such as
the Lock and Event objects. The python queue library provides thread safe queues.
The architecture implemented in python is depicted below:

The implementation closely parallels the SDK10 architecture, with the addition of the Serial Manager layer, whose responsibility it is to communicate serialized GTL messages with the development kit
over the serial port.
Components
ble_devices
The ble_devices directory contains the primary classes enabling a user to interact with the python BLE framework, namely the BleCentral and BlePeripheral classes. These classes provide methods
to exercise BLE functionality for a central or peripheral application respectively.
For example, the BleCentral class implements methods for scanning, connecting, browsing, pairing, reading, writing, etc.
BleCentral and BlePeripheral both inherit from the BleDeviceBase class, which implements functionality common to both central and peripheral devices.
The method signatures of these classes are analogous to their SDK10 counterparts. For example, the scan start function in SDK10 is defined as:
ble_error_t ble_gap_scan_start(gap_scan_type_t type, gap_scan_mode_t mode, uint16_t interval,
uint16_t window, bool filt_wlist, bool filt_dupl)
The scan start function in python is defined as:
def scan_start(self,
type: GAP_SCAN_TYPE = GAP_SCAN_TYPE.GAP_SCAN_ACTIVE,
mode: GAP_SCAN_MODE = GAP_SCAN_MODE.GAP_SCAN_GEN_DISC_MODE,
interval: int = 0,
window: int = 0,
filt_wlist: bool = False,
filt_dupl: bool = False
) -> BLE_ERROR:
The methods exposed by these classes are wrappers for class methods defined in the ble_api. The intent is to provide a single object that encapsulates all the functionality for implementing a BLE central (or peripheral) device.
ble_api
The ble_api directory contains classes that implement the functionality of the Dialog BLE API Library layer. As with SDK10, functionality is broken in into logical groupings:
The BleGapApi class implements GAP related functionality. The BleGattcApi class implements GATT client related functionality. The BleGattsApi class implements GATT service related functionality.
The BleCommonApi class implements common functionality (e.g. reset handling).
In addition, a number of classes and enums are defined for passing parameters / receiving responses and events back from the BLE Framework. Some example include BLE_ERROR, BdAddress, GapScanParams,
GAP_SCAN_TYPE, various BLE event definitions (BleEventGapAdvCompleted, BleEventGapConnected, etc.). Again, these classes and enums are analogous to their SDK10 counterparts.
manager
The manager directory contains classes that implement the functionality of the BLE Manager layer.
The BLE Manager layer is concerned with:
Processing commands from the ble_api and converting them to GTL messages that are passed to the
BleAdapter.Processing events (in the form of GTL messages) from the
BleAdapterand converting them into events understood by the ble_api.
Functionality of the BLE Manager layer is broken into 5 main classes:
The BleManager class orchestrates command and event processing. When the BleManager is initialized, two daemon threads are created. One to receive and process commands from the ble_api,
and a second to receive and process events from the BleAdapter.
When a command or event is received, the BleManager forwards it to the appropriate handler implemented in one of the processing classes: BleManagerGap, BleManagerGattc, BleManagerGatts, or BleManagerCommon
The BleManagerGap class processes GAP related commands and events. The BleManagerGattc class processes GATT client related commands and events.
The BleManagerGatts class processes GATT service related commands and events. The BleManagerCommon class processes common commands and events (e.g. stack reset handling).
adapter
The adapter directory contains classes that implement the functionality of the BLE Adapter layer, specifically the BleAdapter class.
The BLE Adapter layer is concerned with:
Converting GTL messages from the [BleManager](#manager) to byte streams and passing them to the
SerialStreamManagerfor transmission over the serial portConverting byte streams received from the [SerialStreamManager](#serial_manager) into GTL messages for consumption by the
BleManager
When the BleAdapter is initialized, two daemon threads are created. One to receive and process commands from the BleManager, and a second to receive and process bytes streams from the SerialStreamManager.
serial_manager
The serial_manager directory contains classes that implement the functionality of the Serial Manager layer, specifically the SerialStreamManager class.
The Serial Manager layer is concerned with:
Transmitting byte streams from the [BleAdapter](#adapter) over the serial port
Receiving byte streams over the serial port from the DA14xxx development kit and providing them to the
BleAdapterfor consumption.
When the SerialStreamManager is initialized, two daemon threads are created. One to receive byte streams from the BleAdapter and transmit them over the serial port,
and a second to receive byte streams over the serial port and forward them to the BleAdapter.
gtl_messages
The gtl_messages directory contains classes implementing various GTL messages defined in the GTL User Manual A generic base class for every message is defined in gtl_message_base.py
class GtlMessageBase():
def __init__(self,
msg_id: GAPM_MSG_ID = GAPM_MSG_ID.GAPM_UNKNOWN_TASK_MSG,
dst_id: KE_API_ID = KE_API_ID.TASK_ID_INVALID,
src_id: KE_API_ID = KE_API_ID.TASK_ID_INVALID,
par_len: int = 0,
parameters: object() = None ):
self.msg_id = msg_id
self.dst_id = dst_id
self.src_id = src_id
self.par_len = par_len
self.parameters = parameters
This message definition is consistent with the the GTL message format from the user manual:

Separate python files exist for messages related to different BLE layers. For example, gtl_message_gapm.py defines GAP Manager related GTL messages.
Each message takes care of setting the appropriate MSG_ID, DST_ID, SRC_ID, and PAR_LEN for its specific message type. A user only needs to provide the appropriate parameters to create a valid message. The parameters are
one of the LittleEndianStructure’s defined in gtl_port.
For example, below demonstrates creating a GapmResetCmd using the gapm_reset_cmd parameters:
reset_cmd = GapmResetCmd(parameters = gapm_reset_cmd(GAPM_OPERATION.GAPM_RESET))
If no parameters are specified when the message is created, default parameters will be created. The parameters can then be modified after construction as demonstrated in the GapmSetDevConfigCmd below:
set_dev_cmd = GapmSetDevConfigCmd()
set_dev_cmd.parameters.operation = GAPM_OPERATION.GAPM_SET_DEV_CONFIG
set_dev_cmd.parameters.role = GTL_GAP_ROLE.GAP_ROLE_PERIPHERAL
set_dev_cmd.parameters.att_cfg = 0x20
set_dev_cmd.parameters.max_mtu = 512
set_dev_cmd.parameters.max_txoctets = 251
set_dev_cmd.parameters.max_txtime = 2120
In addition, the gtl_messages directory contains factory classes for creating GTL messages from byte streams. For example, the GattcMessageFactory
class coverts byte streams into the appropriate GATT client related GTL message. These are leveraged by the BleAdapter to create valid GTL messages from byte streams received over the serial port.
gtl_port
The gtl_port directory is a port of files with GTL structure and enum definitions from their corresponding .h files in the SDK. Each .h file has a corresponding .py file:
co_bt.h -> co_bt.py
co_version.h -> co_version.py
gap.h -> gap.py
gapm_task.h -> gapm_task.py
rwble_hl_error.h -> rwble_hl_error.py
rwip_config.h -> rwip_config.py
etc.
The C enums defined in these .h files are defined as Python IntEnums in the corresponding .py file.
For example, the c enum gapm_addr_type defined in gapm_task.h:
/// Device Address type Configuration
enum gapm_addr_type
{
/// Device Address is a Public Address
GAPM_CFG_ADDR_PUBLIC,
/// Device Address is a Random Static address
GAPM_CFG_ADDR_PRIVATE,
GAPM_CFG_ADDR_STATIC = GAPM_CFG_ADDR_PRIVATE,
/// Device Address generated using Privacy feature in Host
GAPM_CFG_ADDR_PRIVACY,
/// Device Address generated using Privacy feature in Controller
GAPM_CFG_ADDR_PRIVACY_CNTL = 0x4,
};
is now GAPM_ADDR_TYPE defined in gapm_task.py:
# Device Address type Configuration
class GAPM_ADDR_TYPE(IntEnum):
# Device Address is a Public Address
GAPM_CFG_ADDR_PUBLIC = 0
# Device Address is a Random Static address
GAPM_CFG_ADDR_PRIVATE = auto()
GAPM_CFG_ADDR_STATIC = GAPM_CFG_ADDR_PRIVATE
# Device Address generated using Privacy feature in Host
GAPM_CFG_ADDR_PRIVACY = auto()
# Device Address generated using Privacy feature in Controller
GAPM_CFG_ADDR_PRIVACY_CNTL = 0x4
The C structures defined in these files are ported to python classes. Each of these classes inherits from the Python ctypes library LittleEndianStructure class. The python ctypes library is used to simplify converting these data types into the appropriate byte sequence for transmission over the serial port.
For example, the c structure struct gapm_operation_cmd in gapm_task.h:
/// Operation command structure in order to keep requested operation.
struct gapm_operation_cmd
{
/// GAP request type
uint8_t operation;
};
is now class gapm_operation_cmd(LittleEndianStructure) in gapm_task.py:
# Operation command structure in order to keep requested operation.
class gapm_operation_cmd(LittleEndianStructure):
def __init__(self, operation: GAPM_OPERATION = GAPM_OPERATION.GAPM_NO_OP):
self.operation = operation
super().__init__(operation=self.operation)
# GAP request type
_fields_ = [("operation", c_uint8)]
Note a constructor has been added to the class definition, though this is not required by the ctypes library. This is added for two reasons
To aid in type hinting
It is difficult to know from the type of each Structure field alone what values are appropriate for the field, as the fields are often generic types such as uint8_t, uint16_t, etc. Using a constructor allows us to utilize type hinting to aid a developer in passing in appropriate arguments when creating these structures. For example when creating a
gapm_operation_cmdtheoperationfield, which is defined as ac_uint8, is hinted as aGAPM_OPERATIONenum: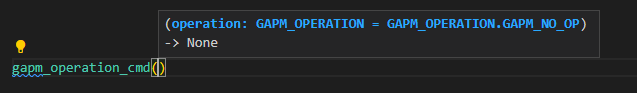
Using this constructor allows us to define default arguments for each Structure. This allows a developer to either create a Structure with the appropriate parameters on construction, or create the Structure and update the fields later.
For example:
example_1 = gapm_operation_cmd(GAPM_OPERATION.GAPM_RESET) example_2 = gapm_operation_cmd() example_2.operation = GAPM_OPERATION.GAPM_RESET