1. Introduction to CodeLess
1.1. Before You Start
Download the latest CodeLess SDK from the Codeless reference page and SmartSnippets™ Toolbox from the SmartBond™ Development Tools web page.
The Codeless SW package content section in the Appendix Section 11 describes the SDK directory structure, gives explanation about folders and their content
Download any local Terminal, such as TeraTerm, Termite, or any other you are familiar with
Arrange for a temperature sensor for performing some examples described in the following chapters. We use Adafruit MCP9808 I2C Temperature sensor, the Thermo 8 Click board™ from MIKROE could be also used.
Make sure the USB driver is installed correctly and the properties of the USB driver look similar to Figure 1. Go to Device Manager, right-click the correct USB serial port, and click Properties > General. Otherwise, you can install FTDI driver from http://www.ftdichip.com/Drivers/VCP.htm.
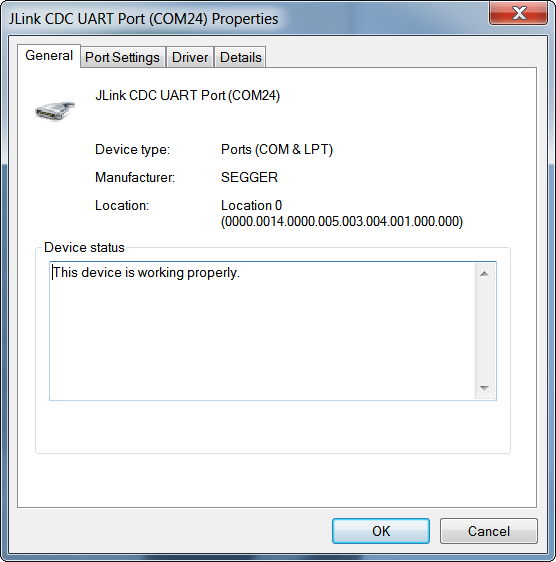
Figure 1 Correctly Installed USB Driver
1.2. CodeLess Objectives
Important
Document Updates for v6.380.20.6x Release
The latest features and enhancements introduced in the recent CodeLess v6.380.20.6x release are detailed below:
Migrating CodeLess to the latest SDK (6.0.22.1401).
The LLVM and the IAR compilers along with e2 Studio and IAR Embedded Workbench respectively can be used to build and run the CodeLess reference design.
Note
e2 studio support To start building a fully working solution on e2 studio and Codeless you can refer to the e² studio SDK 6 Getting Started Guide.
The CodeLess development allows you to quickly get started with wireless IoT applications using a set of AT Commands:
Currently supports our DA1453x/DA1458x SoCs
Enabling control of hardware interfaces as well as Bluetooth® Smart via simple AT command interface
Control of the local as well as remote peer device with a single command set
Completely configurable hardware setup. No SW development required
Great for sensor evaluation (I2C or Analog input port)
Can be easily expanded
Both central and peripheral roles supported in one firmware
Available as source code, hex, and binary files as well as header file for implementation into an external microcontroller
Can be integrated easily in a 3rd party Microcontroller
Table 1 presents the differentiation among the variants of the DA14531-0x.
BLE Features |
DA14531-00 |
DA14531-01 |
DA14535 |
|---|---|---|---|
LE Central support |
YES |
NO |
YES |
LE Observer support |
YES |
NO |
YES |
support the LL Privacy feature (privacy on the controller side) |
YES |
NO |
NO |
Compatible with SDK 6.0.12 or higher |
YES |
NO |
NO |
Compatible with SDK 6.0.18 |
YES |
YES |
NO |
Compatible with SDK 6.0.22 or higher |
YES |
YES |
YES |
Rest of features |
YES |
YES |
YES |
Note
The DA14530 is pin-for-pin compatible with the DA14531 and provides cost savings by operating from an internal LDO, eliminating the cost of a DC/DC inductor.
Note
The SmartBond™ DA14586 is a SoC with an integrated Flash (2 Mbit). The DA14586 is pin-to-pin compatible with the DA14585
The supported boards are:
DA1458x Pro Motherboard - DA1458x daughterboard
DA14531-00FXDEVKT-P Pro Motherboard (supports both DA1453x and DA1458x devices) with:
DA14530-00 daughterboard
DA14531-00 daughterboard
DA14531-01 daughterboard
DA14531MOD daughterboard
DA14535 daughterboard
DA14535MOD daughterboard
DA1458x daughterboard
DA14535-00FXDEVKT-P Pro Motherboard (supports ONLY DA1453x devices) with:
DA14531-00FXDEVKT-P Pro Motherboard with:
DA14530-00 daughterboard
DA14531-00 daughterboard
DA14531-01 daughterboard
DA14531MOD daughterboard
DA14535 daughterboard
DA14535MOD daughterboard
DA1458x Basic board
Any other custom board using DA145xx with a two wire UART will also work
1.3. Highlighting Features
Besides a basic set of AT commands to read and control Bluetooth® LE functions and interface configuration, CodeLess support the following features:
Implements a dedicated mode to exchange seamlessly binary data between devices
Supports several additional AT commands (Bluetooth® LE and interfaces configuration, security, signal indication, PWM etc.)
Configurable to execute a set of existing commands when certain events occur (on connection, on disconnection, on wake-up etc.)
Has over the air firmware update capabilities (SUOTA)
Fully manages the bonding database (import/export entries, clear database, set persistency etc.)
Supports various Bluetooth® LE security scenarios (ranging from secure connections to no security at all)
Supports sleep mode scenarios
Works with SPI command interface in addition to UART/remote Bluetooth® LE device
Supports non–volatile storage for selected commands
Host support: Graphical user interface written in Python/mobile phone application
1.4. Overview of the User Manual
Implementation of CodeLess examples to get an idea of its vast application capabilities and ease of use
Implementation of Binary mode
Use of SmartConsole Android application
Use of Renesas’s Codeless Host application
The examples that will be covered are:
Toggle LED on local board
Read ADC on local board
Write/Read I2C (using I2C Temperature sensor) on local board
Advertise/Scan/connect to the remote board
Toggle LED on remote board
Read ADC on remote board
Write/Read I2C on remote board
CodeLess can be used for more applications than are mentioned above. Typical applications are:
UART to UART wireless connection: CodeLess can be controlled from a PC or a 3rd party microcontroller.
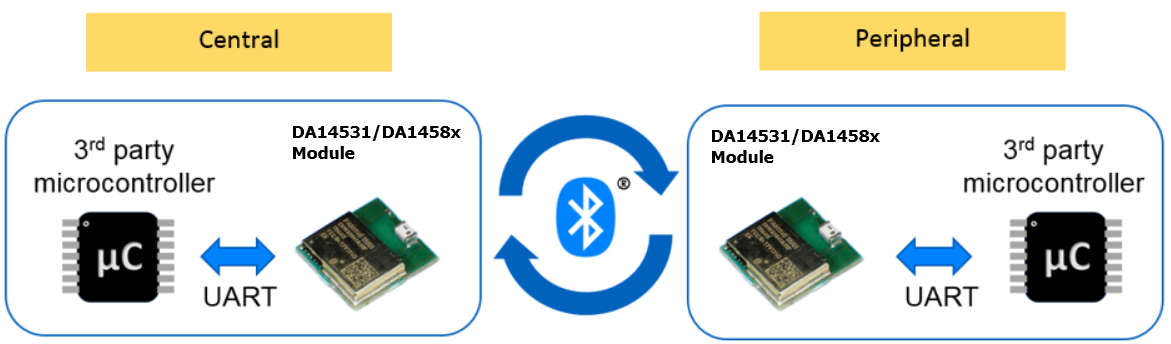
Figure 2 UART to UART Wireless Connection
Warning
The DA14531-01 can’t be configured as a central, to run this demo you should consider the DA14531-00.
Remote access of Peripheral from the Central: The IO control, sensors, and analog signals connected on the peripheral device can be remotely accessed from the Central device.
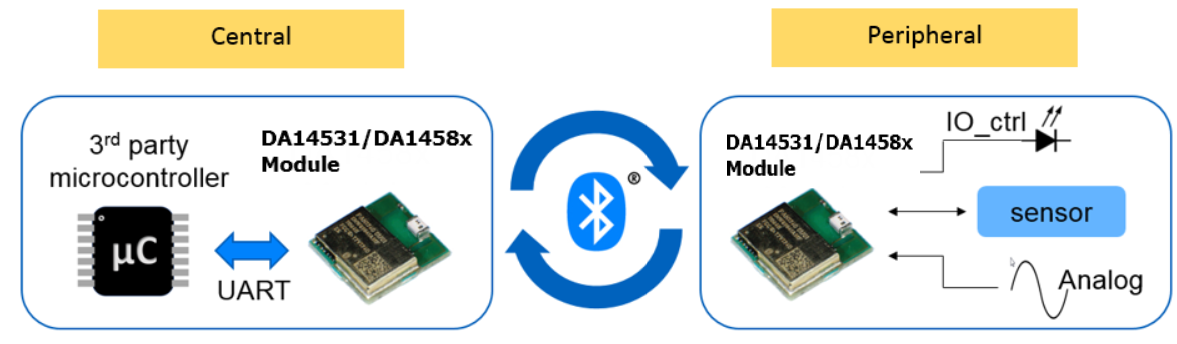
Figure 3 Remote Access of Peripheral from the Central
Warning
The DA14531-01 can’t be configured as a central, to run this demo you should consider the DA14531-00.
CodeLess for debugging: Local connection to the CodeLess for debugging and evaluation of sensor or other connected hardware is easily implemented.
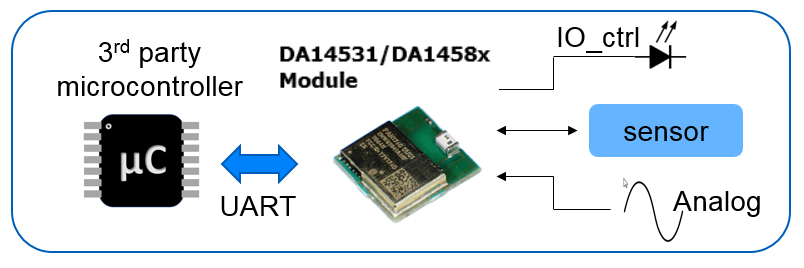
Figure 4 CodeLess for Debugging
Smartphone control of the peripheral.

Figure 5 Smartphone Control of the Peripheral
1.5. Where is it Applicable?
Simplest Bluetooth® LE product implementation
Accelerating time to market for Simple Bluetooth® LE pipe applications connected to an external MCU
Rapid prototyping and Proof of Concept
Sensor evaluation
Renesas’s platform evaluation and introduction to SDK
Platform for further development
Hardware debugging