4. Retrieve Application Code
4.1. Code Retrieval sequence
The procedure used by the ROM Booter to retrieve the firmware from the UART is described in Figure 3.
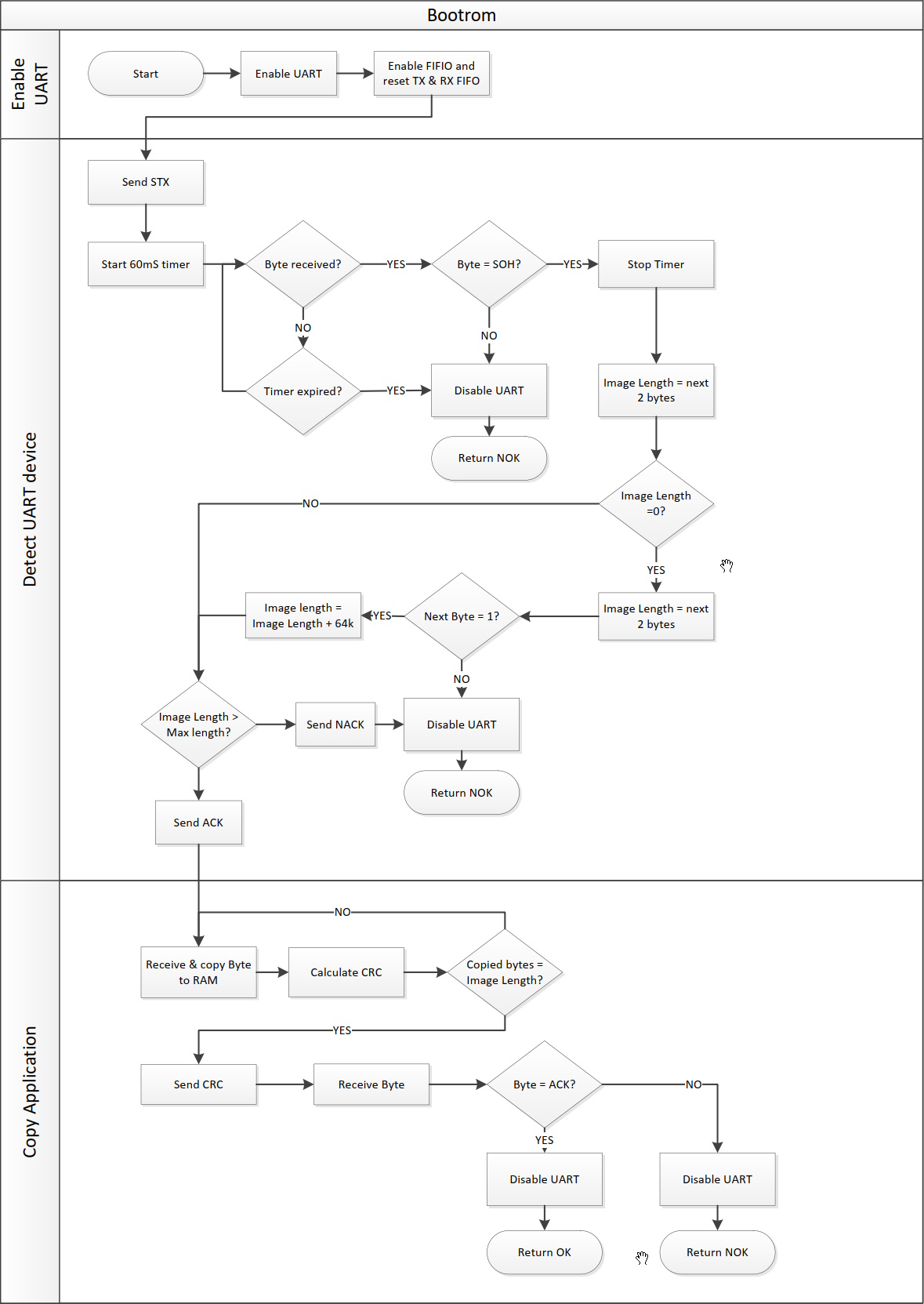
Figure 3 Get Firmware from UART
4.2. Code Retrieval Protocol
The Booter ROM code uses the protocol defined in Table 2. In the protocol the external host should wait to receive the STX byte and then initiate the programming sequence. The length is only two bytes. This limits the size of the bootable image to 64 kBytes.
Byte # |
DA14x9x UTX |
DA14x9x URX |
|---|---|---|
0 |
STX = 0x02 |
|
1 |
SOH = 0x01 |
|
2 |
LEN_LSB |
|
3 |
LEN_MSB |
|
4 |
ACK = 0x06 or NACK = 0x15 |
|
5 .. N |
SW code Bytes |
|
N + 1 |
CRC |
|
N + 2 |
ACK |
If the image is bigger than 64 kBytes and less than 128 kBytes, the protocol described in Table 3 should be used.
Byte # |
DA14x9x UTX |
DA14x9x URX |
|---|---|---|
0 |
STX = 0x02 |
|
1 |
SOH = 0x01 |
|
2 |
0x00 |
|
3 |
0x00 |
|
4 |
LEN_LSB |
|
5 |
LEN_MiddleSB |
|
6 |
LEN_MSB |
|
7 |
ACK = 0x06 or NACK = 0x15 |
|
8 .. N |
SW code Bytes |
|
N + 1 |
CRC |
|
N + 2 |
ACK |
4.3. Boot time
Since the baudrate of the ROMbooter is fixed to 115200 baud, the bootime can take some time. As an example the time it takes to boot an image of 36kB takes about 3.3 seconds (see Figure 4).
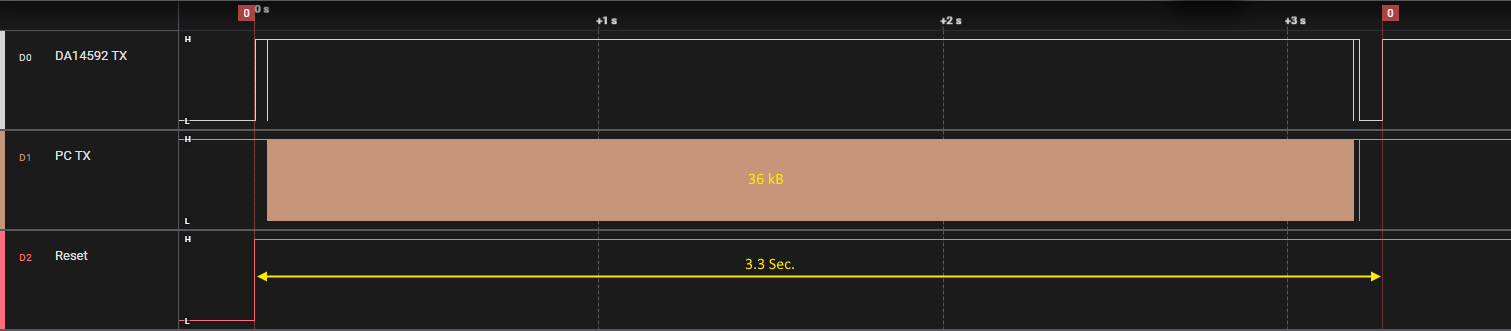
Figure 4 Serial Boot Time
An example of a secondary bootloader is uartboot.bin, which is part of the SDK.